
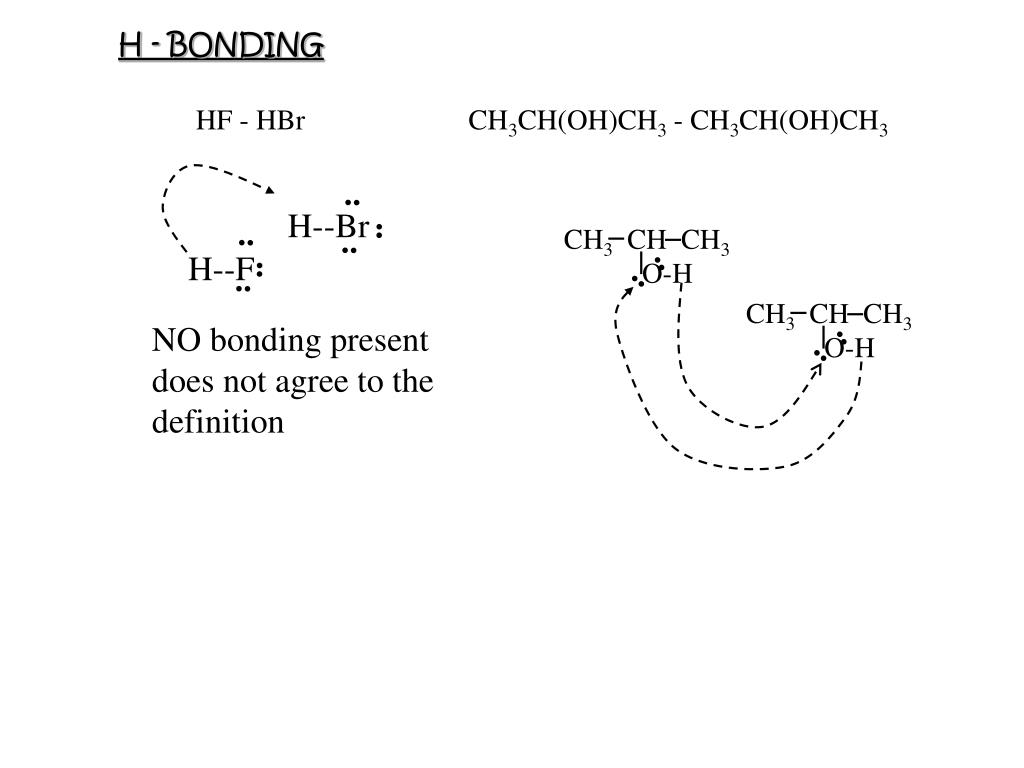
The examples given in the first two rows are similar in that the molecules or atoms are spherical in shape and do not have permanent dipoles. It is very important to apply this rule only to like compounds. Large molecules have more electrons and nuclei that create van der Waals attractive forces, so their compounds usually have higher boiling points than similar compounds made up of smaller molecules. The formula of each entry is followed by its formula weight in parentheses and the boiling point in degrees Celsius. The following table illustrates some of the factors that influence the strength of intermolecular attractions. Thus, in order to break the intermolecular attractions that hold the molecules of a compound in the condensed liquid state, it is necessary to increase their kinetic energy by raising the sample temperature to the characteristic boiling point of the compound.

A clear conclusion to be drawn from this fact is that intermolecular attractive forces vary considerably, and that the boiling point of a compound is a measure of the strength of these forces. Experience shows that many compounds exist normally as liquids and solids and that even low-density gases, such as hydrogen and helium, can be liquified at sufficiently low temperature and high pressure. As temperature is increased, there is a corresponding increase in the vigor of translational and rotation motions of all molecules, as well as the vibrations of atoms and groups of atoms within molecules. It should be noted that there are also smaller repulsive forces between molecules that increase rapidly at very small intermolecular distances.įor general purposes it is useful to consider temperature to be a measure of the kinetic energy of all the atoms and molecules in a given system. If there were no van der Waals forces, all matter would exist in a gaseous state, and life as we know it would not be possible. This attractive force has its origin in the electrostatic attraction of the electrons of one molecule or atom for the nuclei of another. boiling points, melting points and solubilities) are due to intermolecular interactions.Īll atoms and molecules have a weak attraction for one another, known as van der Waals attraction. Indeed, many of the physical characteristics of compounds that are used to identify them (e.g. Since all observable samples of compounds and mixtures contain a very large number of molecules ( ca.!0 20), we must also concern ourselves with interactions between molecules, as well as with their individual structures. Our chief focus up to this point has been to discover and describe the ways in which atoms bond together to form molecules. The molecule is the smallest observable group of uniquely bonded atoms that represent the composition, configuration and characteristics of a pure compound.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
